Bariatric (Weight Loss) Procedures
Weight loss surgery can dramatically improve your health and allow for a better quality of life. As you lose excess weight, you will have more energy and feel proud of the way you look. Feelings of self-confidence will replace feelings of self-consciousness. In addition, bariatric surgery improves most health conditions associated with obesity, and many patients no longer have a need for medications related to these comorbidities. It is important to remember that weight loss surgery is not for everyone, but it is a tool to be used in conjunction with diet and exercise to achieve a healthier and fuller life.
Sleeve Gastrectomy
The sleeve gastrectomy, often referred to as the gastric sleeve, is one of the most commonly performed bariatric procedures today due to its effectiveness and relative simplicity. In this surgery, a large portion of the stomach is removed, leaving behind a narrow, tube-shaped stomach that significantly reduces food capacity. By decreasing stomach size and altering gut hormones that regulate appetite, patients feel full after smaller meals and experience less hunger throughout the day. While it does not involve rerouting the intestines, the sleeve gastrectomy has proven highly effective for weight loss and for improving conditions such as diabetes and high blood pressure.
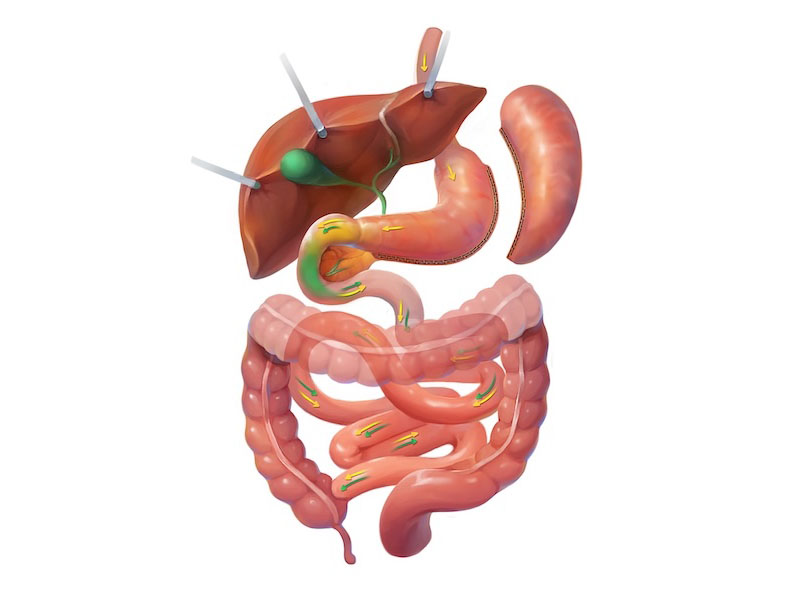
Gastric Bypass
The Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, first performed by Dr. Edward Mason more than 50 years ago, remains widely recognized as the gold standard in bariatric surgery. The procedure involves creating a small stomach pouch and rerouting a portion of the small intestine, which limits how much food a patient can eat and alters digestive hormone signals that influence hunger and satiety. This dual effect allows patients to lose weight by consuming smaller meals and experiencing less hunger, while also improving obesity-related conditions such as type 2 diabetes and high blood pressure. Because of its long track record of safety and effectiveness, it continues to be one of the most commonly performed weight loss surgeries worldwide.
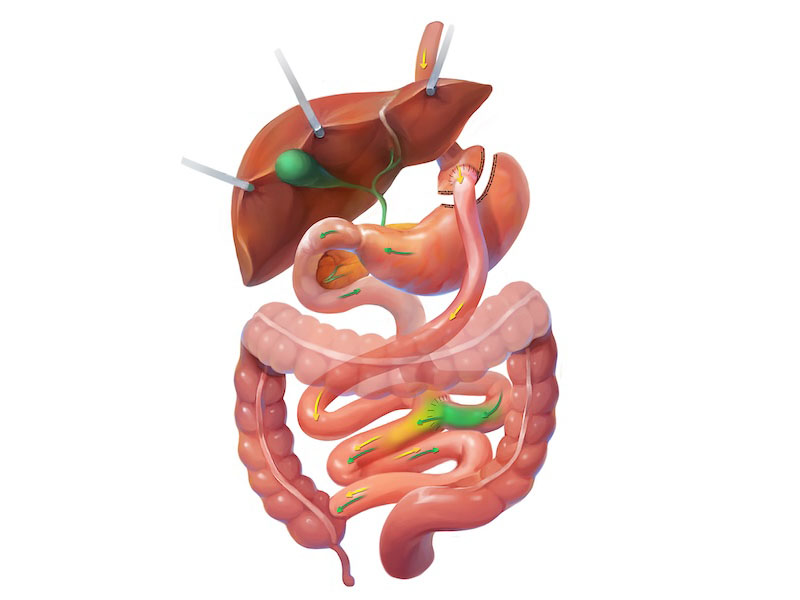
Duodenal Switch
The duodenal switch, also known as biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch, is a powerful bariatric procedure that combines restriction and malabsorption to achieve significant and long-lasting weight loss. It begins with a sleeve gastrectomy to reduce stomach size, followed by rerouting a large portion of the small intestine to limit calorie and nutrient absorption. Patients not only eat less but also absorb fewer calories, particularly from fat, which contributes to substantial weight reduction and marked improvements in obesity-related conditions such as type 2 diabetes and high cholesterol. While highly effective, this surgery requires lifelong commitment to vitamin supplementation and medical follow-up to prevent nutritional deficiencies.
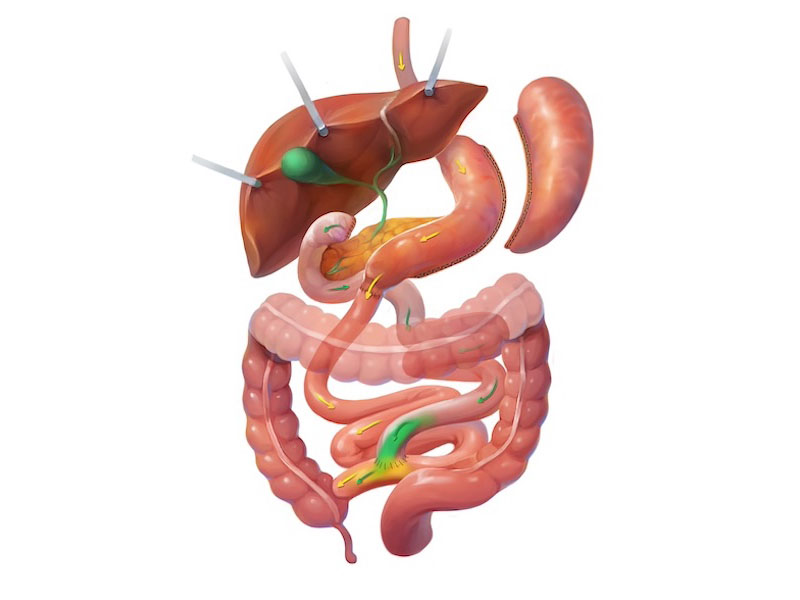
SADI
The SADI-S, or Single Anastomosis Duodeno-Ileal Bypass with Sleeve Gastrectomy, is a newer modification of the traditional duodenal switch designed to provide similar benefits with a simpler surgical technique. Like the duodenal switch, it begins with a sleeve gastrectomy, but instead of two intestinal connections, it uses only one, reducing surgical complexity while still combining restriction and malabsorption. This approach results in significant weight loss, improved satiety, and remission or improvement of many obesity-related diseases such as diabetes and sleep apnea. As with other malabsorptive procedures, patients must commit to lifelong nutritional supplementation and regular monitoring to maintain health over the long term.

