Duodenal Switch (DS)
How We've Improved the DS
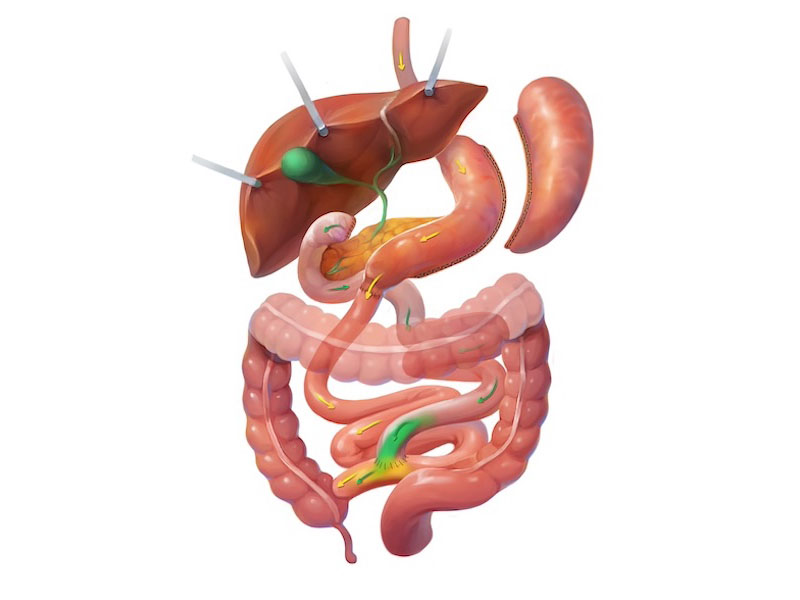
The duodenal switch works by creating a sleeve gastrectomy for restriction and hunger control. Then, the intestines are rerouted, a process similar to that of a gastric bypass. The ideal common channel distance in a DS has changed significantly over time. Initially, this number was 50-100 cm, and while it provided excellent weight loss, it left patients with nutritional deficiencies and diarrhea. We currently target a common channel length of 300 cm for most procedures. Deviations from this number depend on the patient’s needs, and this appears to be the sweet spot where weight loss remains excellent with fewer downsides.
Surgery takes approximately an hour and a half, and patients experience a similar recovery time to that of other procedures. The dietary progression is the same. Food enters the sleeve and is held there with the pylorus, like how a sleeve functions. Because of this, dumping syndrome does not occur, unlike the gastric bypass.
Ideal Patient & Expectations
The ideal patient for a duodenal switch has a significant amount of weight to lose. We know that patients will lose more weight than with other surgical options, particularly patients with a BMI over 50. Patients can expect to lose 80-90% of excess weight in the first year or two after a duodenal switch operation.*
In summary, the duodenal switch offers:
- Greatest weight loss potential of all bariatric procedures
- Minimal risk of dumping syndrome
- Excellent diabetes control
- Minimal risk of ulcer disease. This is particularly helpful for patients who need to take NSAIDs such as aspirin or ibuprofen.
Patients may also wish to research the single “connection” duodenal switch known as the Single Anastomosis Duodeno-Ilestomy or SADI.
Need to Know About the DS
Duodenal Switch Risks & Disadvantages
- Standard surgical risks
- Increased risk of reflux disease
- Greater risk of nutrition deficiencies if not compliant – Vitamin supplementation is important.
- Nausea and vomiting
- Leaks from the staple line
- Reflux
- Small Bowel Obstruction
- Patients may have increased bowel movements
Duodenal Switch Recovery Timeline
- Hospital stay is typically 24 to 48 hours
- Many patients return to regular activity within 1 to 2 weeks
- Heavy lifting is restricted for roughly 4 weeks
*Results will vary between patients

